Residency Program - Case of the Month
May 2015 - Presented by Dr. Amir Ghorbani & Dr. Mirna Lechpammer
History:
17-year-old female with past medical history of Anomalous Pulmonary Venus Connection (Left to right shunt) and Biphasic thoracolumbar Scoliosis with Restrictive Lung Disease. She present with proximal muscle weakness since last year. She has trouble going up and down stairs. She was noted to have a typical scoliotic curve (progressive scoliosis of her spine which has steadily progressed). She has trouble with high impact/high cardio activities (She has a vascular malformation in her venous studies about her arteries and veins around her heart).
Review of systems notable for easy fatigue, chest pains, heart murmur, difficulty exercising, shortness of breath and weakness in her proximal extremities. She denies any numbness or tingling in her bilateral lower extremities. No change in her bowel or bladder habits.
Physical Examination:
Motor testing of her lower extremities revealed 3+/5 hip flexion. She has got 5/5 knee flexion and knee extension. Her EHL and dorsiflexion are 3/5, and her plantar flexion is 4/5. She is unable to walk on her toes or her heels, and unable to arise from a squatted position, although her gait is not grossly abnormal on observational gait. She has no clonus about the ankles and intact sensation L3-S1 bilaterally. Focused examination of her spine shows a 14-degree left-sided hump on forward bending in the lumbar region, 2-degree right hump in the thoracic region, noted levoscoliosis of the lumbar spine. The thoracic curve is much more subtle.
Imaging:
MRI findings suggestive of paraspinal muscle edema and EMG findings suspicious for underlying myopathy process. Also was noted, partial anomalous pulmonary venous return with left to right shunt.
Xray: Plain films are reviewed that do show a significant thoracolumbar curve, which seems to be the dominant entity measured at approximately 45-degree Cobb angle with significant rotation.
Laboratory:
Creatine Kinase (CK) level was normal: 68 (Reference range: 0-250 U/L)
Genetic testing showed a Dynamin 2 (DNM2) gene abnormality located on chromosome 19.
Surgical Pathology:
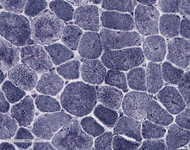
Microscopic Description of muscle biopsy (Left vastus lateralis):
Examination of paraffin-embedded section shows excess variability in fiber size, frequent myonuclei in the center of the muscle fibers, often forming chains when viewed longitudinally. There is no inflammation. These findings are confirmed on H&E frozen section including, small rounded to polygonal fibers, marked excess variability in fiber size, with scattered hypertrophic and hypercontracted fibers. Internalized nuclei are markedly increased, frequently located in the center of myofiber. Some fibers have internalized nuclei more randomly located throughout the fibers. On transverse section, the number of muscle fibers containing central myonuclei is 44% and they appear in both fiber types. Few regenerating fibers are seen. Degenerating fibers, angulated, split fibers or nuclear bags are not present. Myophagocytosis is not present. Inflammatory infiltrates are not seen. Trichrome stain highlights moderate increase in endomysial connective tissue, and rare necrotic fibers. Rimmed vacuoles are not present. Rare fibers contain central red stippling, however definitive ragged red fibers are not seen. Making allowance for the architectural abnormality of the muscle the PAS is normal. Oil-red-O is difficult to interpret related to the fat in the muscle, but is likely normal. NADH histochemistry shows increased reaction in the center of some fibers. ATPase (pH 9.8, 4.6, 4.3) histochemical stains show good differentiation of fiber types which reverse appropriately with pH. Small type I fiber predominate (more than 90%) and type II fibers are normal in size or hypertrophic. There is no fiber type grouping. Esterase stain is increased in some fibers. Acid phosphatase is increased in some myofibers. Alkaline phosphatase and myophosphorylase are within normal limits. SDH stain shows pattern similar to NADH preparation and no overexpressing fibers. COX histochemical stain reveals normal expression pattern in both fiber types. Negative fibers are not observed. Staphylococcal protein A-horseradish peroxidase conjugates stain for immune complexes is negative. Examination of trichrome stains reveals many nerve twigs with preserved myelination.
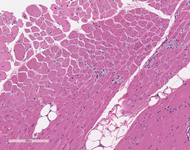 |
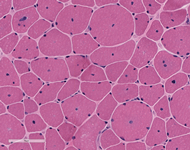 |
|
| H&E Stains | H&E Stains | |
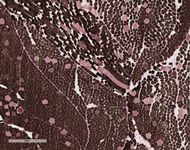 |
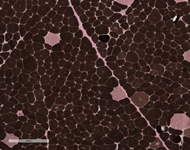 |
|
| ADPase Stain with PH 4.6 | ADPase Stain with PH 4.6 | |
 |
||
| NADH Stain |

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director
 LeShelle May
LeShelle May Chancellor Gary May
Chancellor Gary May